Recently, one of our salespeople pointed out an ad for carbon brushes in a trade publication. The ad made the bold claim that these brushes are "The Industry's BEST Grounding Solution". While it makes for great advertising, the claim requires detailed scrutiny.
Rather than get into the specific details on which the brush manufacturer based its claim, we think it makes sense to compare carbon brushes to AEGIS® Shaft Grounding Rings across a full range of performance criteria.
Grounding Effectiveness
While carbon brushes provide adequate shaft grounding for DC  motors (and low-frequency currents), they are far less effective for the high-frequency currents found in inverter-fed AC motors. Due to their very small surface contact (less than 4% of the shaft's circumference), current does not flow uniformly across the brush surface. It flows through a series of very small contact spots, leading to high impedance and hotspotting.
motors (and low-frequency currents), they are far less effective for the high-frequency currents found in inverter-fed AC motors. Due to their very small surface contact (less than 4% of the shaft's circumference), current does not flow uniformly across the brush surface. It flows through a series of very small contact spots, leading to high impedance and hotspotting.
In contrast, AEGIS Rings have hundreds of thousands of shaft contact points spread 360 degrees around the shaft. By maximizing the contact area, AEGIS Rings maximize the high-frequency discharge capability for VFD-induced voltage.
Hotspotting & High Wear
Since current does not flow uniformly across carbon brushes' contact faces, they are susceptible to "hotspotting". Current passes only in very small areas at any single point in time, so the high current density of these discharges generates very high temperatures (hotspotting) that lead to high brush wear.  With AEGIS Rings, the hundreds of thousands of contact points spread around the shaft circumference transfer current evenly, eliminating hotspotting and the excessive, nonuniform wear they cause.
With AEGIS Rings, the hundreds of thousands of contact points spread around the shaft circumference transfer current evenly, eliminating hotspotting and the excessive, nonuniform wear they cause.
Carbon brushes work only when they are in physical contact with the motor shaft. The specially engineered conductive microfibers of AEGIS Rings, however, have unique mechanical and electrical characteristics that ensure effective electrical contact with the motor shaft — even if physical contact is broken. Their patented Nanogap technology maintains electrical contact with the shaft across gaps from 2 nm to 5µm.
Carbon brushes are only effective for DC motors and low-frequency currents. AEGIS Rings, however, are specially designed to protect motors against high-frequency discharges, up to the kHz and MHz range, as produced by VFDs.
Surface Rate:
While high surface rates produce faster wear of carbon brushes leading to more frequent replacements, the effectiveness of AEGIS Rings has been proven in testing at surface rates greater than 180 ft/second and 50,000 RPMs. Spring energized carbon brushes wear quickly and lose contact with the shaft without maintenance or replacement. AEGIS microfibers however have virtually zero friction in contact with the shaft, and even at high rotational speeds AEGIS Rings can be expected to outlive the bearings.
Tolerance to Environmental Conditions:
Environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and the pressure of the brush against the motor shaft can limit the effectiveness of carbon brushes. In fact, even the build-up of carbon from the brush itself on the surface of the shaft can create a highly resistive film that can interfere with the brush's grounding effectiveness for high-frequency shaft voltage.
Carbon brushes are also sensitive to humidity to maintain a conductive patina on the motor shaft. Too little humidity and the carbon dust won't stick to the shaft, leading to higher friction, brush vibration, and faster wear. Too much humidity can lead to an overly thick film, which can cause grooves in the brush, further reducing its contact with the shaft and lessening its effectiveness.
Carbon brushes are also easily fouled by dirt, dust, grease, and other contaminants that can jam spring-loading mechanisms or disrupt electrical contact between the shaft and the brush.
AEGIS Rings, on the other hand, provide the highest level of resistance to contaminants of any shaft grounding technology. Their microfibers are designed to “sweep” contaminants away from the shaft to maintain contact. And installing the ring inside the motor provides added protection from contamination, for the longest lasting and highest performance possible in highly contamination-prone applications.
level of resistance to contaminants of any shaft grounding technology. Their microfibers are designed to “sweep” contaminants away from the shaft to maintain contact. And installing the ring inside the motor provides added protection from contamination, for the longest lasting and highest performance possible in highly contamination-prone applications.
Service Life:
Due to wear, carbon brushes require periodic replacement over the course of the bearings' lifetime. But AEGIS Rings are designed to last for the full L10 life of the bearings, due to AEGIS microfibers' special design.
The microfibers are designed for minimum wear and maximum conductivity. After 10,000 hours of testing, the fibers showed wear of less than 0.001" and are projected to last over 200,000 hours of continuous operation and to withstand 2 million reversals. Even when the fibers are worn down to fit the shaft exactly, AEGIS Nanogap Technology ensures that the fibers continue to work by non-contact electron transfer.
Finally, since they last for the L10 bearing 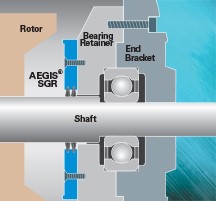 life of the motor and they do not generate any dust or contamination, AEGIS Rings can be installed inside motors — they can be bolted to the back of the bearing retainer. Internal installation will not interfere with the operation of the motor or the AEGIS Ring's performance, yet offers an extra measure of protection for the ring itself.
life of the motor and they do not generate any dust or contamination, AEGIS Rings can be installed inside motors — they can be bolted to the back of the bearing retainer. Internal installation will not interfere with the operation of the motor or the AEGIS Ring's performance, yet offers an extra measure of protection for the ring itself.
AEGIS Rings just work. So for the world's most effective bearing protection — regardless of motor size, horsepower, speed, or service requirements (stops/starts/reversals) — insist on AEGIS Shaft Grounding Rings, proven in millions of installations worldwide.
For a technical bulletin comparing the effectiveness of carbon block brushes to that of AEGIS Rings, click here.
For our IEEE paper on AEGIS Rings, Design Aspects of Conductive Microfiber Rings for Shaft Ground Purposes, click here.

